OpenClaw 429 rate limit errors occur when your AI provider's quota is exhausted or when you've exceeded the requests-per-minute threshold. Unlike authentication errors that point to configuration problems, a 429 error means your setup is correct—you've simply hit the provider's capacity limits. The good news is that this is almost always a temporary condition with several effective solutions, from simply waiting 60 seconds to configuring intelligent fallback models that automatically switch providers when limits are reached.
Quick Diagnosis - Find Your Problem in 60 Seconds

When you encounter a 429 error in OpenClaw, the first step is identifying exactly what type of rate limit you've hit. Not all 429 errors are the same—some indicate you've exhausted your monthly quota entirely, while others simply mean you need to wait a few seconds before your next request. Understanding this distinction determines whether you need an immediate workaround or a longer-term solution.
The fastest way to diagnose your situation is running openclaw models status in your terminal. This command reveals the current state of all configured providers, showing which ones are in cooldown, their remaining capacity, and when they'll become available again. If you see a provider marked as "cooling down" with a timestamp, you know exactly how long to wait before that provider accepts requests again.
Diagnostic Commands to Run Immediately
Start with these three commands to get a complete picture of your situation:
bashopenclaw models status # Deep health check with provider verification openclaw status --deep # Auto-fix common configuration issues openclaw doctor --fix
The output from openclaw models status tells you whether your rate limit is temporary (cooldown active) or quota-based (daily/monthly limit reached). If you see "cooldown" in the status, the solution is usually waiting or switching providers. If you see "quota exhausted," you'll need to either upgrade your API tier or configure alternative providers.
Distinguishing 429 from Other Errors
Before diving into rate limit solutions, make sure you're actually dealing with a 429 error. The error message should contain rate_limit_error or too_many_requests. If you see authentication_error instead, you're dealing with an API key issue—check our guide on troubleshooting the Anthropic API key error for that scenario. Configuration errors like invalid headers produce different error codes entirely.
A genuine 429 error response looks like this:
json{ "error": { "type": "rate_limit_error", "message": "You have exceeded your rate limit. Please retry after 60 seconds." } }
TL;DR
Rate limit errors in OpenClaw happen when you exceed your AI provider's request quotas. Here's what you need to know:
- Immediate fix: Wait 60 seconds for the token bucket to refill, or restart OpenClaw gateway to clear cooldowns
- Short-term solution: Configure fallback models in
openclaw.jsonso requests automatically route to backup providers - Long-term prevention: Upgrade your API tier (Anthropic Tier 4 offers 80x more capacity than Tier 1), implement retry logic with exponential backoff, and distribute load across multiple providers
- Known bugs to watch: OpenClaw's exponential backoff is documented but may not work as expected (Issue #5159), and a single model hitting limits can trigger cooldown for the entire provider (Issue #5744)
- Key commands:
openclaw models status(check cooldowns),openclaw status --deep(verify providers),openclaw doctor --fix(auto-repair)
Immediate Fixes - Restore Service Fast
When your AI assistant stops responding due to rate limits, you need solutions that work right now. Here are three approaches ranked by how quickly they restore service, starting with the fastest option that requires zero configuration changes.
Option 1: Wait for Token Bucket Refill (60 seconds)
Most AI providers use a token bucket rate limiting system that continuously refills. If you've hit a temporary rate limit rather than exhausting your daily quota, simply waiting 60 seconds often resolves the issue. During this time, the bucket refills with new request capacity. You can monitor the countdown with openclaw models status—watch for the cooldown timer to reach zero.
This approach works best when you've made a burst of requests in a short period. The provider hasn't blocked you; it's just asking you to slow down. Token bucket systems are designed to allow bursts followed by recovery periods, so this temporary pause is expected behavior rather than a sign of a configuration problem.
Option 2: Restart the Gateway to Clear Cooldowns
OpenClaw maintains internal cooldown state that persists until it naturally expires. If you need immediate access and can't wait for the timer, restarting the OpenClaw gateway process clears all cooldown states:
bash# Stop and restart OpenClaw openclaw stop openclaw start # Or if using the background service systemctl restart openclaw # Linux brew services restart openclaw # macOS
After restarting, the gateway treats all providers as fresh, with no cooldown history. This is particularly useful when cooldowns were triggered by a bug (like Issue #5744 where a single model can trigger full provider cooldown) rather than actual rate limit responses from the provider.
Option 3: Switch to an Available Provider
If you have multiple AI providers configured, you can immediately route requests to one that isn't rate-limited. Check which providers are available:
bashopenclaw models status
Look for providers showing "available" status. You can then either manually specify that provider in your request or rely on OpenClaw's automatic fallback if configured. For Claude users hitting Anthropic limits, switching to OpenAI or Google's models provides immediate relief while your Anthropic quota recovers.
Understanding Rate Limits by Provider
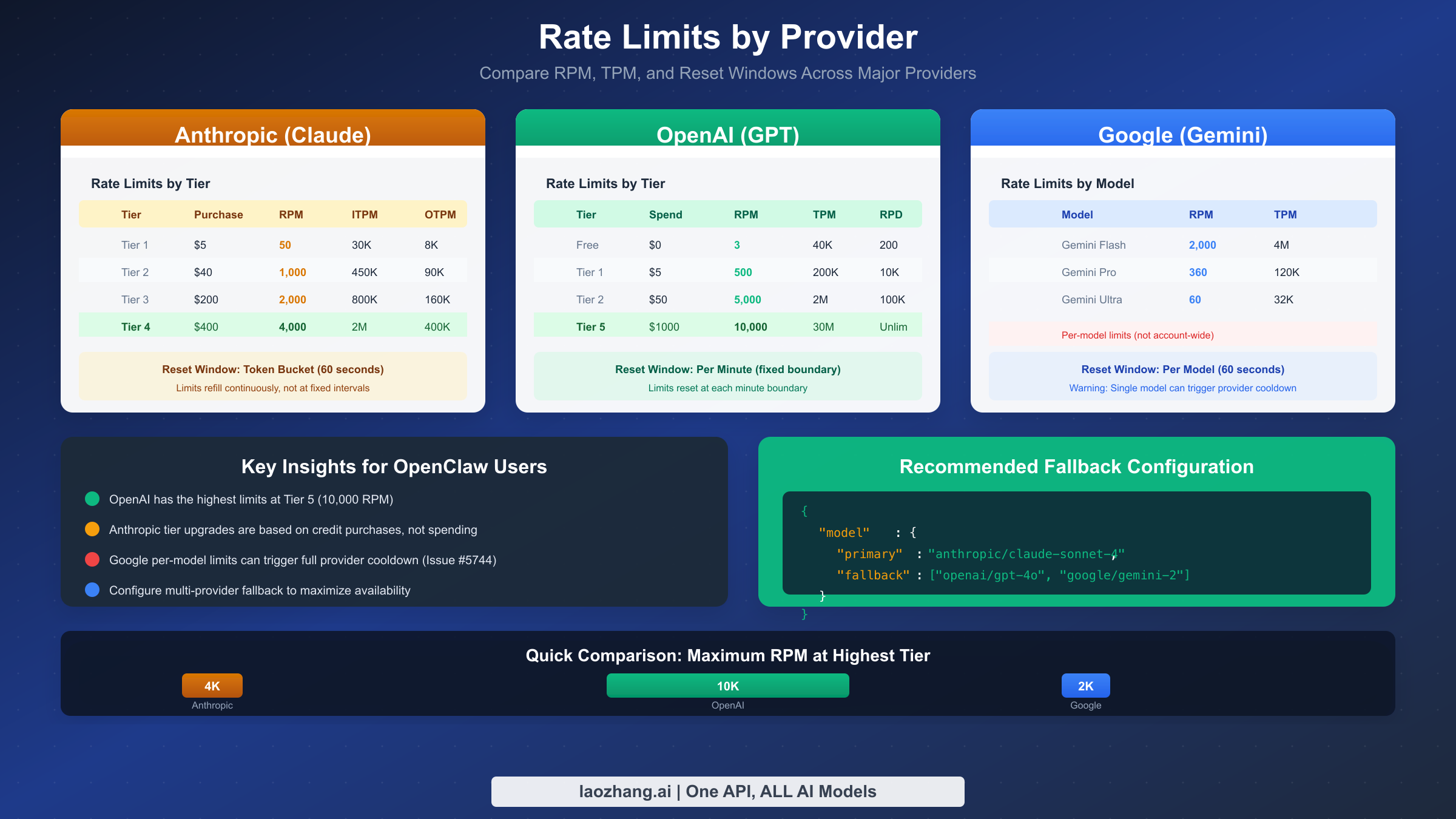
Each AI provider implements rate limiting differently, with varying tiers, limits, and reset behaviors. Understanding these differences helps you choose the right provider for your workload and configure appropriate fallbacks when one provider reaches capacity.
Anthropic (Claude)
Anthropic uses a tier-based system where your spending history determines your limits. New accounts start at Tier 1 with modest limits, and tiers increase automatically as you spend more:
| Tier | Cumulative Spend | Requests/Min | Input Tokens/Min (Sonnet) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Tier 1 | $5 | 50 | 30,000 |
| Tier 2 | $40 | 1,000 | 450,000 |
| Tier 3 | $200 | 2,000 | 800,000 |
| Tier 4 | $400 | 4,000 | 2,000,000 |
The jump from Tier 1 to Tier 4 represents an 80x increase in request capacity. If you're regularly hitting Anthropic rate limits, checking your current tier through the Anthropic Console should be your first step. Many developers operate at Tier 1 without realizing that a small additional purchase would dramatically increase their limits.
OpenAI (GPT-4, GPT-4o)
OpenAI's limits are also tier-based but with different thresholds:
| Tier | Requirements | Requests/Min | Tokens/Min |
|---|---|---|---|
| Free | New account | 3 | 40,000 |
| Tier 1 | $5 paid | 500 | 200,000 |
| Tier 2 | $50 paid | 5,000 | 2,000,000 |
| Tier 3 | $100 paid | 5,000 | 4,000,000 |
| Tier 5 | $1,000 paid | 10,000 | 30,000,000 |
OpenAI's free tier is extremely limited at just 3 requests per minute, making it unsuitable for any real workload. Even the basic Tier 1 at $5 spent provides a 166x improvement in request capacity.
Google (Gemini)
Google's Gemini API has both free and paid tiers:
| Tier | Requests/Min | Requests/Day | Tokens/Min |
|---|---|---|---|
| Free | 15 | 1,500 | 32,000 |
| Pay-as-you-go | 2,000 | Unlimited | 4,000,000 |
The free tier's 1,500 requests per day limit makes it suitable as a backup provider but not a primary one for active development. The paid tier removes daily limits entirely.
Strategic Provider Selection
For maximum availability, consider using API proxy services like laozhang.ai that aggregate multiple providers and handle rate limiting at the proxy layer. These services can automatically route requests to available providers, effectively multiplying your total capacity across all configured backends.
Configuring Model Fallback
The most robust defense against rate limit interruptions is configuring fallback models that automatically activate when your primary provider hits limits. OpenClaw supports sophisticated fallback chains that can route requests through multiple backup providers before failing.
Basic Fallback Configuration
In your openclaw.json configuration file, add a fallback array to your model configuration:
json{ "models": { "claude-sonnet": { "provider": "anthropic", "model": "claude-3-5-sonnet-20241022", "fallback": [ "gpt-4o", "gemini-pro" ] }, "gpt-4o": { "provider": "openai", "model": "gpt-4o" }, "gemini-pro": { "provider": "google", "model": "gemini-1.5-pro" } } }
With this configuration, when Claude hits a rate limit, requests automatically route to GPT-4o. If GPT-4o is also limited, Gemini Pro serves as the final fallback. This creates a three-deep resilience layer that significantly reduces the chance of complete service interruption.
Advanced Fallback with Conditions
For more control, you can specify fallback conditions:
json{ "models": { "claude-sonnet": { "provider": "anthropic", "model": "claude-3-5-sonnet-20241022", "fallback": { "models": ["gpt-4o", "gemini-pro"], "on": ["rate_limit", "timeout", "unavailable"], "maxAttempts": 3 } } } }
The on array specifies which error types trigger fallback. Setting "on": ["rate_limit"] ensures fallback only activates for rate limits, not for other errors that might indicate a configuration problem worth investigating.
Using Proxy Services as Fallback
For professional deployments, consider adding a proxy service like laozhang.ai as an additional fallback layer:
json{ "models": { "claude-sonnet": { "provider": "anthropic", "model": "claude-3-5-sonnet-20241022", "fallback": [ { "provider": "laozhang", "model": "claude-3-5-sonnet", "baseUrl": "https://api.laozhang.ai/v1" }, "gpt-4o" ] } } }
Proxy services maintain their own provider relationships and rate limits independent of yours, providing an additional buffer when your direct API access is limited.
Understanding the Cooldown Mechanism

OpenClaw implements its own cooldown mechanism on top of provider rate limits. Understanding how this internal system works helps you predict when limits will be lifted and avoid configurations that trigger unnecessary cooldowns.
How Cooldowns Get Triggered
When OpenClaw receives a 429 response from any provider, it marks that provider as "in cooldown" for a calculated duration. The documented backoff strategy uses exponential intervals: 1 minute for the first occurrence, then 5, 25, and 60 minutes for subsequent hits within a window. However, Issue #5159 documents that the actual implementation may differ, with some users observing much shorter intervals of 1-27 seconds.
The cooldown applies at the provider level, not the model level. This means if you're using Claude Sonnet and hit a rate limit, Claude Opus will also be marked as unavailable even though Opus has separate rate limits at Anthropic. Issue #5744 tracks this behavior as a known limitation.
Token Bucket vs. Fixed Window
Most providers use token bucket rate limiting, which works differently from fixed-window limits:
-
Token Bucket: Capacity continuously refills at a steady rate. You can make bursts of requests as long as the bucket has tokens, and it refills even while you're making requests. A 60 RPM limit with token bucket means roughly 1 token added per second.
-
Fixed Window: Capacity resets entirely at specific intervals. A 60 RPM limit with fixed windows means you might wait the full minute if you exhaust your allocation early.
Anthropic and OpenAI both use token bucket systems, which is why the standard advice to "wait 60 seconds" often works—the bucket has fully refilled by then, even if you completely emptied it.
Clearing Cooldowns Manually
Since cooldown state lives in the OpenClaw gateway process, restarting the gateway clears all cooldowns immediately. This is safe to do when you believe the cooldown was triggered incorrectly (such as by a bug) or when you've resolved the underlying issue (like upgrading your API tier). After restart, OpenClaw will query providers fresh without any cooldown memory from previous sessions.
bash# View current cooldown states openclaw models status --verbose # Clear all cooldowns by restarting openclaw restart
Known Issues and Workarounds
OpenClaw's rate limit handling has several documented bugs that can cause unexpected behavior. Being aware of these issues helps you distinguish between provider limits and gateway bugs, choosing the appropriate fix for each situation.
Issue #5159: Exponential Backoff Not Working as Documented
The OpenClaw documentation describes exponential backoff intervals of 1, 5, 25, and 60 minutes. However, Issue #5159 reports that actual behavior differs significantly, with observed backoffs as short as 1-27 seconds. This issue was closed as "not planned" for fixing, meaning you cannot rely on the documented backoff behavior.
Workaround: Don't depend on OpenClaw's internal backoff. Implement your own retry logic at the application level (see the Implementing Retry Logic section), or configure fallback models to avoid waiting for backoff entirely.
Issue #5744: Single Model Triggers Full Provider Cooldown
When one model from a provider hits a rate limit, OpenClaw marks the entire provider as in cooldown. This means hitting limits on Claude Sonnet also blocks Claude Opus, even though they have separate rate limits at Anthropic.
Workaround: Configure fallback models from different providers rather than different models from the same provider. A fallback from Claude Sonnet to Claude Opus won't help if both get blocked together.
If you encounter errors related to AWS Bedrock configuration alongside rate limits, check our guide on the invalid beta flag error when using AWS Bedrock—these can sometimes appear together when provider configurations interact unexpectedly.
Issue #4766: Gateway Returns Empty Messages (Fixed)
Earlier versions of OpenClaw would sometimes return empty responses when rate limited instead of proper error messages. This has been fixed in version 2026.1.x and later, but if you're running an older version, you might see silent failures instead of 429 errors.
Workaround: Update to the latest OpenClaw version with openclaw update or check your package manager for updates.
Summary of Known Issues
| Issue | Status | Impact | Workaround |
|---|---|---|---|
| #5159 Backoff not working | Closed (won't fix) | Unpredictable wait times | Implement own retry logic |
| #5744 Full provider cooldown | Open | All models blocked together | Cross-provider fallbacks |
| #4766 Empty responses | Fixed | Silent failures | Update OpenClaw |
| #1004 Embeddings crash | Fixed | Gateway crash on 429 | Update OpenClaw |
Implementing Retry Logic
Since OpenClaw's built-in backoff may not work as expected, implementing your own retry logic provides more reliable recovery from rate limits. Here are production-ready implementations in Python and JavaScript.
Python Implementation with Tenacity
The tenacity library provides robust retry logic with exponential backoff and jitter:
pythonfrom tenacity import retry, wait_random_exponential, stop_after_attempt, retry_if_exception_type import openai # Configure retry for rate limit errors @retry( wait=wait_random_exponential(min=1, max=60), stop=stop_after_attempt(6), retry=retry_if_exception_type(openai.RateLimitError) ) def call_openai(messages): client = openai.OpenAI( base_url="http://localhost:5000/v1", # OpenClaw gateway api_key="your-key" ) return client.chat.completions.create( model="claude-sonnet", messages=messages ) # Usage try: response = call_openai([{"role": "user", "content": "Hello"}]) except openai.RateLimitError: print("Rate limit persisted after 6 retries")
The wait_random_exponential function adds jitter to prevent thundering herd problems where multiple retrying clients all hit the API at the same moment.
JavaScript Implementation
For Node.js applications, implement similar logic with async/await:
javascriptasync function callWithRetry(messages, maxRetries = 6) { let lastError; for (let attempt = 0; attempt < maxRetries; attempt++) { try { const response = await fetch('http://localhost:5000/v1/chat/completions', { method: 'POST', headers: { 'Content-Type': 'application/json', 'Authorization': 'Bearer your-key' }, body: JSON.stringify({ model: 'claude-sonnet', messages: messages }) }); if (response.status === 429) { const retryAfter = response.headers.get('Retry-After') || Math.min(Math.pow(2, attempt) + Math.random(), 60); console.log(`Rate limited, waiting ${retryAfter}s (attempt ${attempt + 1})`); await new Promise(resolve => setTimeout(resolve, retryAfter * 1000)); continue; } if (!response.ok) { throw new Error(`HTTP ${response.status}`); } return await response.json(); } catch (error) { lastError = error; } } throw lastError; }
Best Practices for Retry Logic
When implementing retries, follow these guidelines to avoid making rate limit problems worse:
- Add jitter: Random delays prevent multiple clients from retrying simultaneously
- Respect Retry-After headers: When providers send this header, use its value instead of calculating your own
- Set maximum attempts: Infinite retries can exhaust quotas faster; 5-6 attempts is usually sufficient
- Log retry attempts: Visibility into retry frequency helps identify when you need more capacity
- Consider circuit breakers: After multiple failures, stop retrying temporarily to let the provider recover
Prevention and Optimization
The best approach to rate limits is preventing them from occurring in the first place. These strategies reduce your likelihood of hitting limits and ensure your application degrades gracefully when limits are unavoidable.
Monitor Your Usage Patterns
Run regular checks on your API consumption to identify trends before they become problems:
bash# Check current status across all providers openclaw status --deep # Monitor request patterns over time openclaw logs --filter="429" --since="1h"
If you consistently hit limits at certain times (like business hours), consider implementing request queuing or scheduling intensive operations for off-peak periods.
Optimize Request Efficiency
Reducing the number of API calls directly reduces rate limit pressure:
- Batch operations: Combine multiple questions into single prompts where appropriate
- Cache responses: Store results for identical or similar queries to avoid redundant API calls
- Use streaming wisely: Streaming responses count as single requests but keep connections open longer
- Right-size your models: Use smaller, faster models for simple tasks; reserve powerful models for complex work
Implement Graceful Degradation
Design your application to remain functional even when rate limited:
- Show meaningful waiting states: Instead of generic loading spinners, tell users "High demand - response may take longer"
- Queue non-urgent requests: Let users continue working while background requests wait for capacity
- Offer alternatives: When AI features are limited, fall back to non-AI alternatives where possible
Proactive Capacity Planning
Review your tier levels quarterly and upgrade before hitting limits becomes routine:
- Anthropic: Tier upgrades happen automatically based on spending, but you can prepay to reach higher tiers faster
- OpenAI: Similar automatic progression; monitor your usage dashboard for tier transition timing
- Google: Moving from free to paid tier removes daily limits entirely
For mission-critical applications, maintaining relationships with multiple providers and proxy services like laozhang.ai ensures you always have alternative capacity available.
Frequently Asked Questions
How long should I wait after getting a 429 error?
For most providers using token bucket rate limiting, waiting 60 seconds allows the bucket to fully refill. However, the optimal wait time depends on your specific situation. Check the Retry-After header in the 429 response if provided—this gives you the provider's recommended wait time. If no header is present, 60 seconds is a safe default. For more aggressive recovery, you can try again after 10-15 seconds since token buckets continuously refill.
Can I increase my rate limits without spending more money?
Generally, no—rate limits are tied to your spending tier with most providers. However, you can effectively increase your total capacity by distributing requests across multiple providers. Configuring Claude, GPT-4, and Gemini as fallbacks for each other triples your aggregate capacity without increasing spending with any single provider. Additionally, some providers offer limit increases for enterprise customers who commit to minimum spending levels.
Why does OpenClaw show cooldown when I haven't made many requests?
This typically happens due to Issue #5744, where a single model hitting limits triggers cooldown for the entire provider. Even if you've only used Claude Sonnet, attempting a Claude Opus request could show as rate-limited. The other common cause is stale cooldown state from previous sessions—try restarting the OpenClaw gateway to clear accumulated cooldowns.
Should I implement retry logic if I have fallbacks configured?
Yes, they serve different purposes. Fallbacks route failed requests to alternative providers, giving you immediate continuity. Retry logic attempts the same provider again after a delay, useful when the provider will recover quickly. The ideal setup uses both: fallbacks for immediate availability, plus retry logic within each fallback to handle transient limits. This layered approach maximizes your success rate.
How do I know which tier I'm on with Anthropic or OpenAI?
Both providers display your current tier in their billing dashboards. For Anthropic, visit console.anthropic.com and check the Settings > Limits page. For OpenAI, visit platform.openai.com/account/limits. These pages show your current tier, rate limits, and how much more spending is needed to reach the next tier. If you've just made a payment, tiers typically update within a few hours.
![Fix OpenClaw Rate Limit Exceeded (429): Complete Troubleshooting Guide [2026]](/posts/en/openclaw-rate-limit-exceeded-429/img/cover.png)