OpenClaw's "invalid beta flag" error stops your AI assistant cold when using AWS Bedrock or Google Vertex AI as your Claude provider. The fix is straightforward: set "beta_features": [] in your ~/.openclaw/openclaw.json configuration file. This disables the SDK's automatic beta header injection that these managed services don't support. For most users, this single change resolves the issue immediately—but if you need beta features or have specific requirements, this guide covers all 5 solutions in depth.
TL;DR
Before diving into details, here's what you need to know: The "invalid beta flag" error happens because the Anthropic SDK automatically attaches beta headers that AWS Bedrock and Google Vertex AI reject. The quickest fix is adding "beta_features": [] to your OpenClaw config. If you need beta features like computer-use or extended context, you'll need to switch to direct Anthropic API access. For users seeking cost savings or stable China access, OpenAI-compatible proxies like laozhang.ai provide an alternative path that sidesteps this issue entirely.
Identifying the Invalid Beta Flag Error
The "invalid beta flag" error manifests in several ways depending on your setup, but the core symptoms are unmistakable. Your OpenClaw AI assistant becomes completely unresponsive—messages sent through WhatsApp, Telegram, or other connected platforms return blank or show "(no output)" responses. The gateway logs reveal the underlying cause with error messages that point directly to the beta flag issue.
When examining your logs through openclaw logs --follow, you'll encounter one of these error patterns. AWS Bedrock users typically see "ValidationException: invalid beta flag" in the response body. Google Vertex AI users encounter "400 Bad Request: invalid beta flag" with similar symptoms. The JSON-formatted error response looks like this:
json{ "type": "error", "error": { "type": "invalid_request_error", "message": "invalid beta flag" } }
This error exclusively affects users who have configured AWS Bedrock or Google Vertex AI as their Claude model provider. If you're using direct Anthropic API access, you won't encounter this issue—those endpoints fully support all beta features. The problem arises specifically in the translation layer between OpenClaw and these managed cloud services.
To confirm you're dealing with this specific error rather than a general configuration issue, run openclaw doctor first. This diagnostic command validates your overall setup and can distinguish between authentication problems, network issues, and the beta flag error. If the doctor reports healthy status but Claude-related requests still fail, you're almost certainly facing the beta flag incompatibility.
Quick Fix (Start Here)
The fastest way to resolve this error is modifying your OpenClaw configuration to disable beta features. This approach works for approximately 80% of users because most deployments don't actually require the experimental features that trigger the error. Open your configuration file at ~/.openclaw/openclaw.json and add the beta_features setting under your agents defaults.
Here's the exact configuration change you need to make:
json{ "agents": { "defaults": { "model": { "primary": "anthropic/claude-sonnet-4", "options": { "beta_features": [] } } } } }
After saving the file, restart your OpenClaw gateway to apply the changes. The command openclaw restart handles this cleanly. If you're running OpenClaw as a systemd service or Docker container, use the appropriate restart mechanism for your deployment.
To verify the fix worked, send a test message through your preferred channel—WhatsApp, Telegram, or the web interface. You should receive a normal response from Claude within a few seconds. Additionally, check the logs with openclaw logs --follow while sending the test message. You should no longer see the "invalid beta flag" error in the output.
If the quick fix doesn't resolve your issue, you have an edge case that requires one of the alternative solutions covered in the following sections. Common reasons the simple fix might not work include: your configuration file has a syntax error, you have multiple configuration sources that override each other, or your specific deployment uses a different configuration path. Running openclaw config --show displays your active configuration and helps identify any conflicts.
Understanding Why This Error Occurs
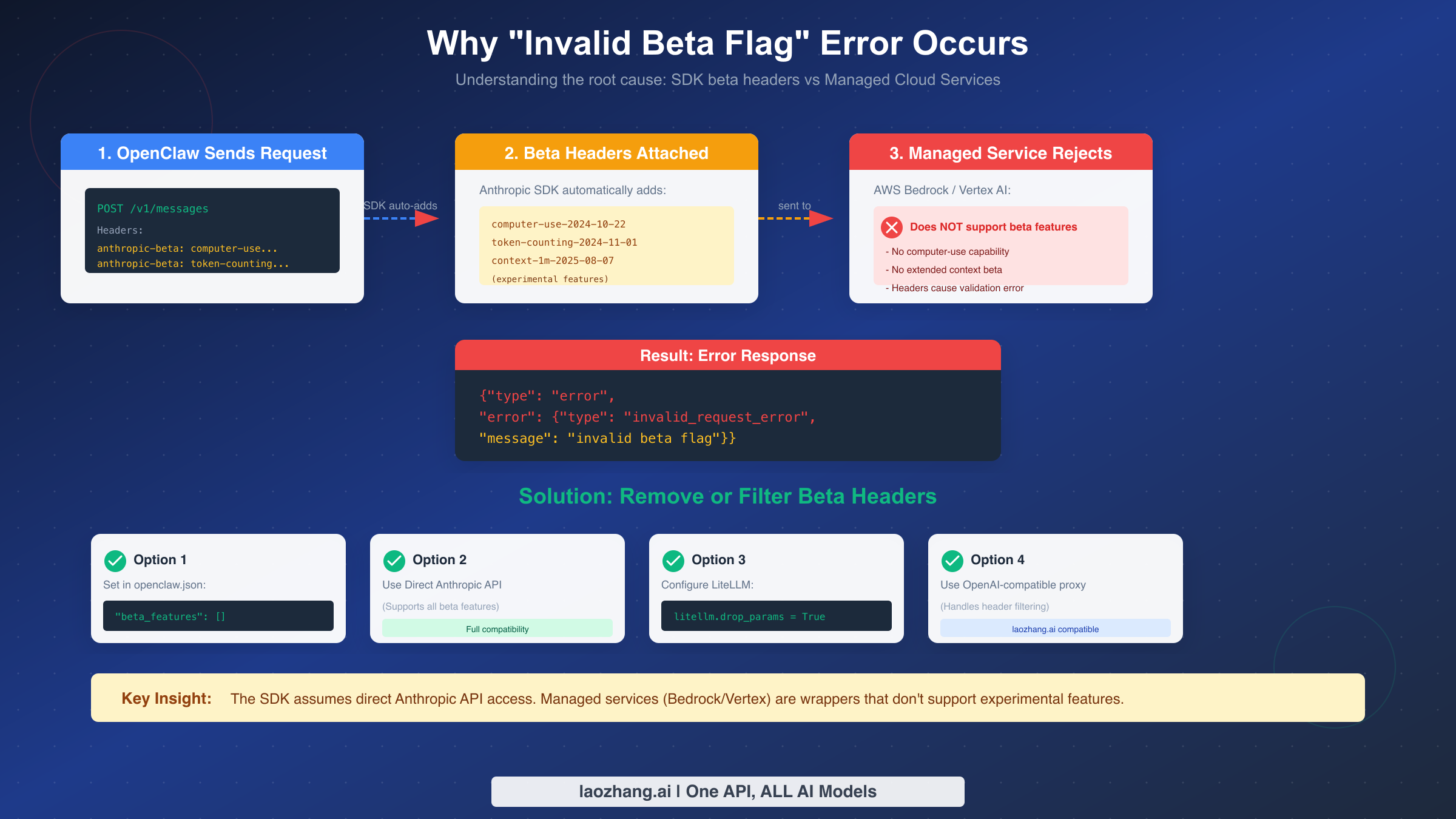
The root cause of this error lies in a fundamental mismatch between what the Anthropic SDK expects and what managed cloud services support. When OpenClaw sends requests to Claude models, the underlying SDK automatically attaches beta headers to enable experimental features. These headers tell the API server which preview capabilities the client wants to use.
The SDK injects several beta headers by default, including computer-use-2024-10-22 for automated browser control, token-counting-2024-11-01 for precise usage tracking, and context-1m-2025-08-07 for extended context windows. These features are valuable for advanced use cases but require direct Anthropic API infrastructure to function.
AWS Bedrock and Google Vertex AI operate as managed wrappers around the underlying Claude models. They provide enterprise-grade features like IAM integration, VPC endpoints, and compliance certifications, but they achieve this by standardizing the API surface. As a result, these services strip out or reject any headers they don't explicitly support—including Anthropic's beta feature flags.
When the Bedrock or Vertex AI proxy receives a request containing these unsupported beta headers, it has no mechanism to handle them gracefully. The only option is to reject the request entirely with an "invalid beta flag" validation error. This error message originates from the cloud provider's validation layer, not from Claude itself.
Understanding this architecture explains why the fix works: by explicitly setting beta_features to an empty array, you're telling the SDK not to attach any beta headers in the first place. The request goes through cleanly because there's nothing for the managed service to reject. However, this also means you lose access to those experimental features—a tradeoff that matters for some use cases.
The LiteLLM library that OpenClaw uses for provider abstraction has configuration options to filter headers at the proxy level, which offers an alternative solution for users who want header filtering without modifying OpenClaw configuration directly. This approach is covered in the solutions section for LiteLLM users.
All 5 Solutions Explained
Each solution addresses the beta flag error from a different angle. Your choice depends on your specific requirements, deployment constraints, and whether you need access to beta features.
Solution 1: Disable Beta Features in OpenClaw Config
This is the recommended approach for most users. Edit ~/.openclaw/openclaw.json and add the beta_features configuration as shown earlier. The key is ensuring the setting appears in the correct location within your config structure. If you're using a custom config path, adjust accordingly.
For verification, send a test request and check logs:
bashopenclaw logs --follow
Look for successful completion without the "invalid beta flag" error. The response should show normal Claude output.
Solution 2: Use Direct Anthropic API
If you need beta features like computer-use for browser automation or extended context windows, direct API access is your only option. Switch your OpenClaw provider configuration to use Anthropic directly:
bashexport ANTHROPIC_API_KEY="your-anthropic-api-key"
Then update your models config to use the anthropic provider:
json{ "models": { "providers": { "anthropic": { "baseUrl": "https://api.anthropic.com", "auth": "api-key" } } } }
This approach gives you full access to all Claude features, including beta capabilities. The tradeoff is losing the enterprise features that Bedrock and Vertex AI provide, such as AWS IAM authentication, VPC endpoints, and compliance certifications specific to those platforms.
Solution 3: Configure LiteLLM Header Filtering
If you're using LiteLLM as a proxy layer (common in complex deployments), you can configure it to filter out problematic headers before they reach the cloud provider. Add these settings to your LiteLLM configuration:
pythonimport litellm litellm.drop_params = True litellm.modify_params = True
For configuration file-based setups, add the equivalent YAML:
yamllitellm_settings: drop_params: true
This approach keeps your existing provider configuration intact while solving the beta header issue at the proxy level. It's particularly useful for deployments where multiple applications share a common LiteLLM proxy.
Solution 4: Disable Prompt Caching
In some cases, the beta flag error is specifically triggered by the prompt caching feature. If you've tried Solution 1 and still encounter issues, try explicitly disabling caching:
json{ "agents": { "defaults": { "model": { "cache": { "enabled": false } } } } }
This is a more targeted fix that preserves other model options while addressing the specific caching-related beta header. However, disabling caching may impact performance for repetitive workloads where cached responses provide latency benefits.
Solution 5: Switch to OpenAI-Compatible Proxy
For users who want to avoid provider-specific issues entirely, OpenAI-compatible proxy services offer an alternative path. These services handle the translation between OpenAI's API format and Claude's native API, filtering out incompatible headers in the process.
Configure OpenClaw to use an OpenAI-compatible endpoint:
json{ "models": { "providers": [ { "name": "proxy", "type": "openai", "baseURL": "https://api.laozhang.ai/v1", "models": ["claude-sonnet-4", "claude-opus-4-5"] } ] } }
This approach provides stable access without worrying about beta header compatibility. Services like laozhang.ai also offer cost advantages and reliable access for users in regions where direct Anthropic API access may be unreliable.
Choosing the Right Solution
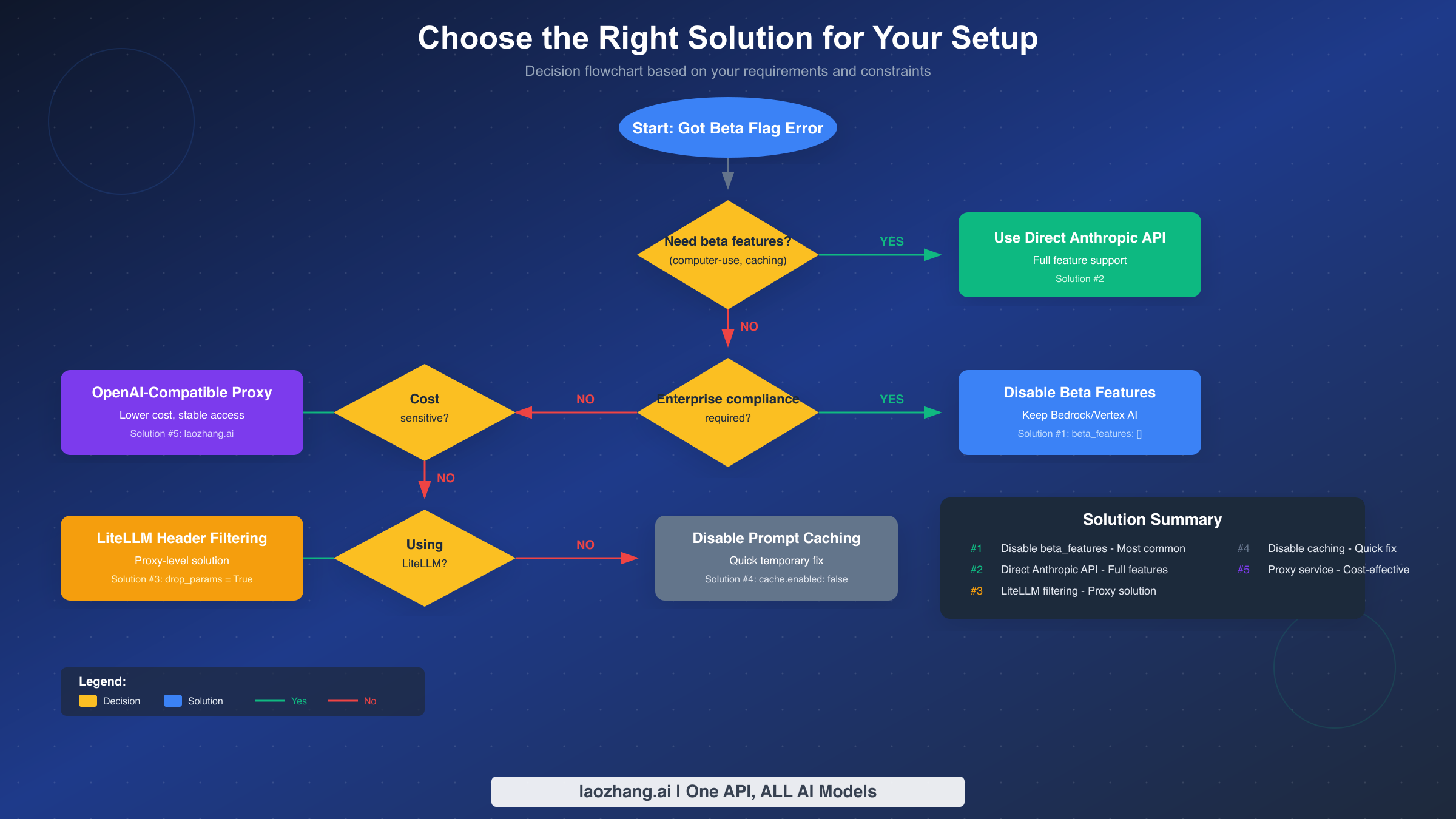
Selecting the appropriate solution depends on answering a few key questions about your requirements. The decision flowchart above provides a visual guide, but here's the logic in detail.
Do you need beta features? If yes, Solution 2 (Direct Anthropic API) is your only option. Beta features like computer-use, token counting, and extended context are exclusive to direct API access. If you don't need these features—and most OpenClaw deployments don't—any of the other solutions will work.
Is enterprise compliance required? If you chose AWS Bedrock or Google Vertex AI specifically for compliance, data residency, or IAM integration, stick with those providers and use Solution 1 or Solution 3. These solutions preserve your enterprise setup while fixing the compatibility issue.
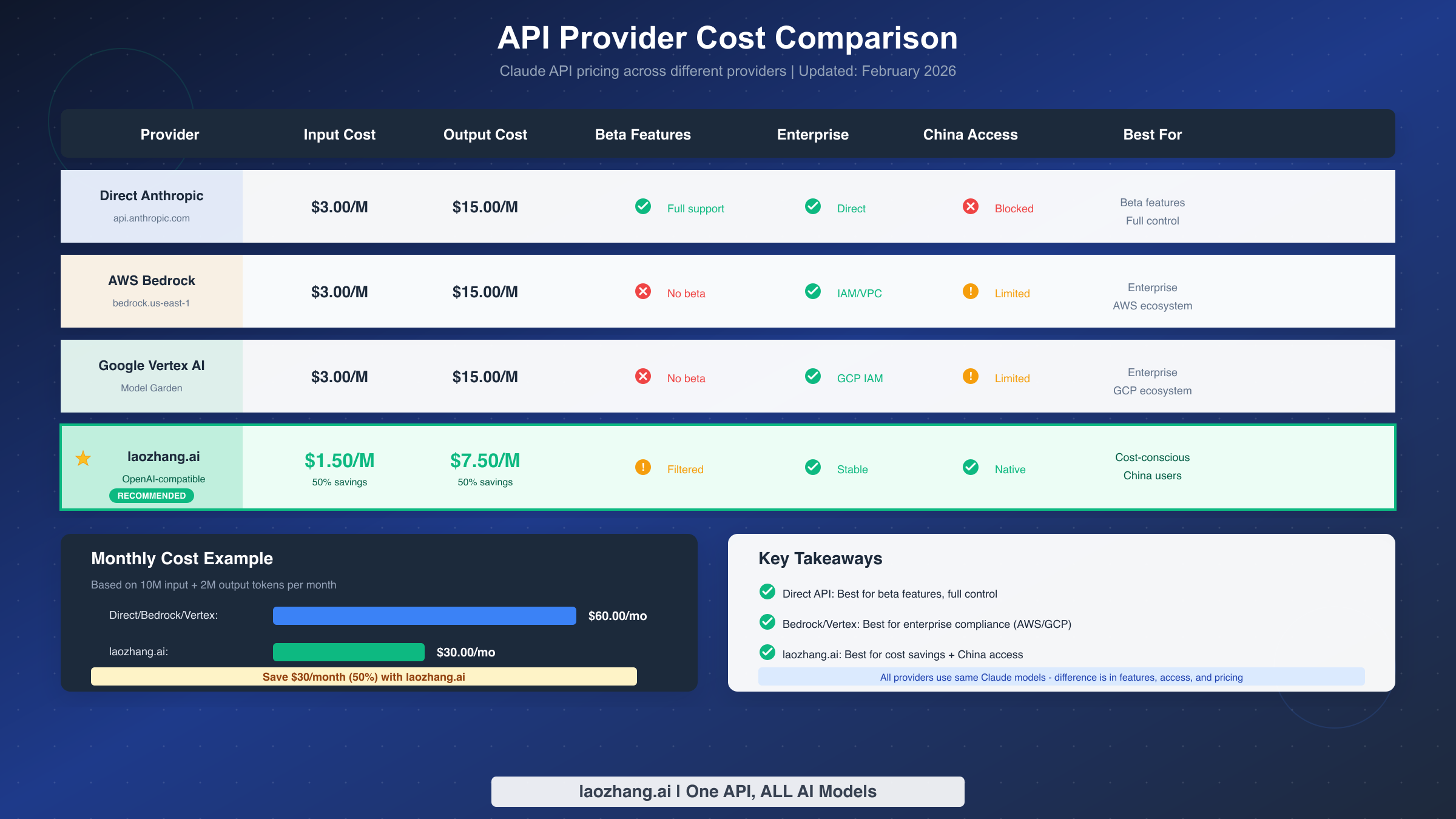
Are you cost-sensitive? If reducing API costs matters more than using a specific provider, Solution 5 with a proxy service offers significant savings. The cost comparison below shows the difference across providers.
Are you using LiteLLM? If your deployment already includes LiteLLM as a proxy layer, Solution 3 provides the cleanest integration. You can solve the problem at the proxy level without modifying OpenClaw configuration.
Need China access? For users in China or regions with connectivity issues to direct Anthropic or cloud provider endpoints, Solution 5 with a proxy service like laozhang.ai provides more reliable access. These services often have infrastructure optimized for regional connectivity.
For most users, the recommendation is straightforward: start with Solution 1 (disable beta_features). It's the simplest fix and works for the vast majority of deployments. Only explore alternatives if you have specific requirements that Solution 1 doesn't address.
Enterprise Deployment Considerations
Enterprise deployments often have constraints that individual users don't face. Compliance requirements, data residency regulations, and security policies may dictate which solutions are acceptable. Understanding these factors helps you make the right choice for your organization.
AWS Bedrock offers several enterprise features that matter for regulated industries. IAM integration provides fine-grained access control. VPC endpoints keep traffic within your AWS network. CloudTrail logging creates audit trails for compliance. If you chose Bedrock specifically for these features, Solution 1 (disabling beta features) preserves your security posture while fixing the error.
Google Vertex AI provides similar enterprise capabilities within the GCP ecosystem. Data residency options, VPC Service Controls, and integration with Google Cloud's IAM system make it attractive for organizations already invested in GCP. Again, Solution 1 works here without compromising your enterprise configuration.
For organizations that can't modify cloud provider settings due to centralized IT policies, Solution 3 (LiteLLM filtering) may be more appropriate. This approach solves the problem at the proxy layer without touching the provider-specific configuration that your IT team manages.
Data residency deserves special attention. If regulations require your AI processing to happen within specific geographic regions, both Bedrock and Vertex AI support regional deployments. Direct Anthropic API may not meet these requirements depending on your jurisdiction. Proxy services vary in their data handling practices—review their documentation and compliance certifications before using them in regulated environments.
When comparing Claude models for your use case, consider that enterprise deployments often benefit from the consistency of managed services even with the beta feature tradeoff. The reliability, compliance certifications, and integration with existing infrastructure usually outweigh the loss of experimental features.
Prevention: Setting Up OpenClaw Right the First Time
Avoiding the beta flag error from the start saves troubleshooting time. When setting up OpenClaw with AWS Bedrock or Google Vertex AI, follow these best practices to prevent the issue before it occurs.
Step 1: Plan your provider choice deliberately. Before installation, decide whether you need enterprise features (Bedrock/Vertex) or beta features (direct API). You can't have both simultaneously. If you're unsure, start with direct API access—it's easier to migrate to a managed service later than to lose functionality you depend on.
Step 2: Configure beta_features proactively. When creating your initial openclaw.json, include the beta_features setting from the start:
json{ "agents": { "defaults": { "model": { "primary": "anthropic/claude-sonnet-4", "options": { "beta_features": [] } } } } }
This prevents the error from ever appearing, even if future OpenClaw updates change default behavior.
Step 3: Validate before going live. After configuration, run openclaw doctor to check your setup. Send test messages through each connected channel to verify end-to-end functionality. Check logs during testing to catch any silent failures.
Step 4: Document your configuration. Record which provider you're using and why. Note any enterprise compliance requirements that drove the decision. This documentation helps future team members understand the constraints when modifications are needed.
Step 5: Stay updated on provider support. Both AWS and Google occasionally update their Claude offerings. Monitor release notes for announcements about beta feature support. The landscape may change, potentially enabling features that weren't previously available.
For teams deploying OpenClaw at scale, consider using configuration management tools to enforce consistent settings across instances. Ansible playbooks, Terraform modules, or Kubernetes ConfigMaps can ensure the beta_features setting is always present in new deployments.
Troubleshooting Tips and FAQ
Even with the right solution applied, edge cases can complicate resolution. These troubleshooting tips address common scenarios that don't follow the standard pattern.
Q: I applied the fix but still see the error. What's wrong?
Multiple configuration sources can override each other. Run openclaw config --show to see your active configuration. Look for beta_features settings that might be coming from environment variables, command-line arguments, or additional config files. OpenClaw merges configuration from several sources, and the wrong one might be taking precedence.
Q: The error appeared after an OpenClaw update. Did something change?
Updates occasionally modify default behavior. Check the release notes for your new version. If beta features were enabled by default in the update, you'll need to explicitly disable them again. Your config file isn't overwritten during updates, but new defaults might be merged differently.
Q: Can I use some beta features but not others?
Yes, the beta_features array accepts specific feature names. Instead of an empty array, you can list only the features you want:
json{ "beta_features": ["token-counting-2024-11-01"] }
However, each feature must be supported by your provider. Test each one individually to find which work with Bedrock or Vertex AI.
Q: Why does my friend's setup work without these changes?
They're likely using direct Anthropic API or an OpenAI-compatible proxy, neither of which has this limitation. The beta flag error is specific to AWS Bedrock and Google Vertex AI. Different providers have different compatibility characteristics.
Q: Is this a bug in OpenClaw or the SDK?
It's a compatibility gap rather than a bug. The Anthropic SDK is designed for direct API access where beta features work. Managed services intentionally restrict features for standardization. OpenClaw sits in the middle, working with whatever provider you configure. The "fix" is really configuration alignment between these components.
Q: Will this issue be fixed in future versions?
Potentially, but not guaranteed. The underlying constraint is that managed services don't support beta features. A future OpenClaw version might auto-detect provider type and adjust header behavior, but that requires coordination between multiple parties. For now, explicit configuration is the reliable approach.
Q: How do I know if I'm using a beta feature without realizing it?
Common beta features include prompt caching, computer-use automation, token counting APIs, and extended context windows. If you're not explicitly using these capabilities in your OpenClaw skills or agents, you likely don't need them. The default OpenClaw installation doesn't require any beta features for basic functionality.
For persistent issues, the OpenClaw community on GitHub Discussions and the project's FAQ documentation provide additional resources. The error is well-documented, and community members often share solutions for unusual configurations.
The "invalid beta flag" error, while frustrating, has straightforward solutions once you understand the underlying cause. Whether you disable beta features, switch providers, or use a proxy service, the path to a working OpenClaw deployment is clear. Choose the solution that matches your requirements, apply the configuration, and your AI assistant will be back online.
![Fix OpenClaw Invalid Beta Flag Error: Complete Guide [2026]](/posts/en/openclaw-invalid-beta-flag/img/cover.png)