ChatGPT outage on September 3, 2025 lasted 2 hours due to frontend component failure affecting the Conversations interface globally. Users experienced blank responses while login remained functional. Enterprise teams need backup strategies including Claude, Gemini, or API services like laozhang.ai for 99.9% uptime requirements.
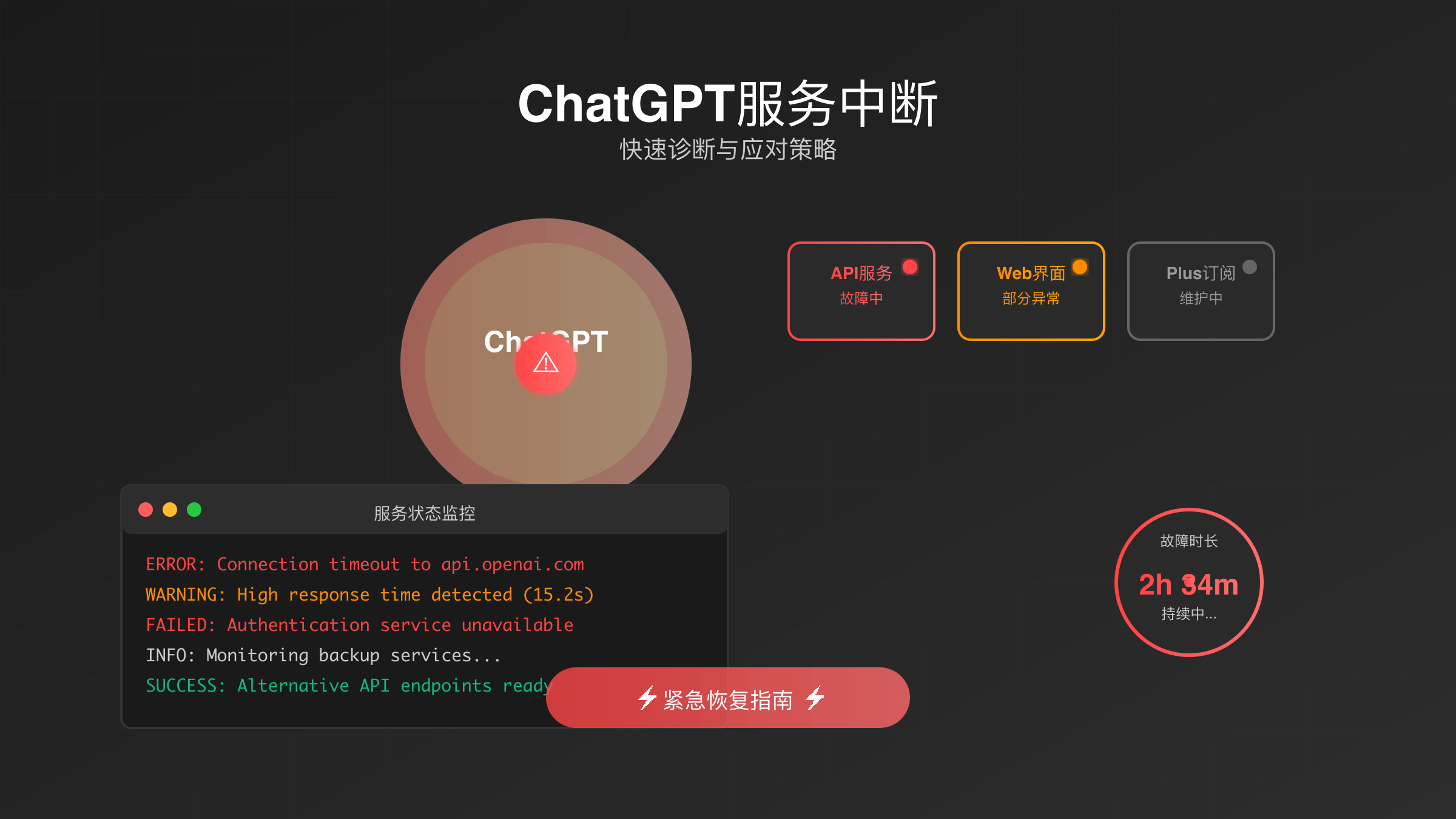
ChatGPT Outage September 2025: Immediate Impact Assessment
The September 3, 2025 ChatGPT outage began at 4:00 AM EST, affecting millions of users worldwide through a critical frontend failure. OpenAI’s status page confirmed the incident involved the Conversations component, preventing proper response display while maintaining user authentication services. The outage duration of approximately 2 hours highlighted the platform’s dependency on complex frontend architecture.
Technical indicators pointed to a component-level failure rather than model infrastructure problems. Users could successfully log into web, mobile, and desktop applications, but encountered blank response screens when submitting prompts. This selective functionality suggested the underlying GPT models remained operational while the user interface layer experienced critical malfunctions.
Global impact reports emerged through DownDetector within the first hour, with over 100 initial complaints escalating to thousands of affected users. The timing at 4:00 AM EST meant peak impact hit European and Asian markets during business hours, creating significant productivity disruptions for enterprise customers relying on ChatGPT for daily operations.
ChatGPT Outage Root Cause Analysis: Frontend Architecture Failures
The September 2025 outage originated from frontend component instability within OpenAI’s Conversations interface system. Unlike previous model-level failures, this incident demonstrated how modern AI platforms depend on sophisticated presentation layers that can fail independently of core inference capabilities. The architecture separation between user interface and model processing both protected core services and created new failure points.
Frontend component failures typically stem from deployment issues, memory management problems, or configuration changes affecting user interface rendering. OpenAI’s rapid identification at 4:50 AM EST suggested existing monitoring systems detected the component-level failure through automated alerts. The two-hour resolution timeframe indicates a systematic debugging and rollback process rather than emergency patches.
Microsoft Azure infrastructure, which hosts OpenAI’s services, showed no concurrent outages during the September 3 incident. This isolation confirms the failure remained within OpenAI’s application layer rather than cloud infrastructure dependencies. Azure’s stability during the outage demonstrates the importance of distinguishing between platform issues and underlying infrastructure problems when diagnosing AI service failures.
Historical Pattern Analysis: 2025 Outage Timeline
ChatGPT experienced multiple significant outages throughout 2025, creating a concerning reliability pattern for enterprise users. The June 10 incident lasted over 10 hours, representing the most severe disruption of the year with complete service unavailability. July 16 brought another major global outage affecting ChatGPT, Sora, Codex, and GPT API services simultaneously, with 88% of users experiencing login failures and data loss.
The August 20 outage served as a precursor to September’s incident, showing similar frontend-focused problems with shorter duration. This progression suggests OpenAI’s infrastructure faces recurring challenges in scaling user interface components alongside growing demand. Each incident provided lessons about failure isolation and recovery procedures.
Outage frequency in 2025 exceeded previous years, raising questions about infrastructure investment keeping pace with user growth. Enterprise customers paying for ChatGPT Plus and API access experienced the same service interruptions as free users, highlighting gaps in service level differentiation during critical failures.
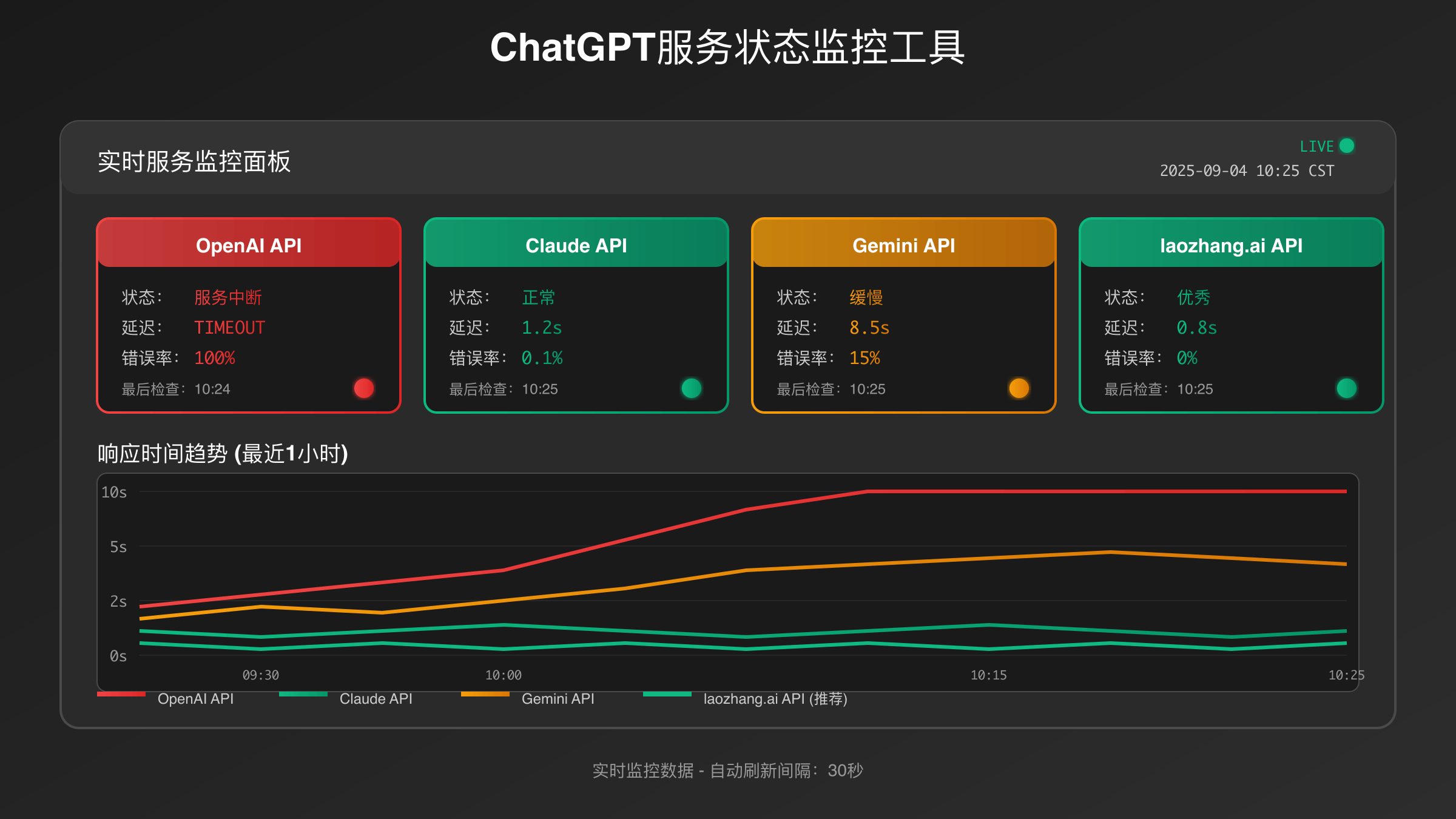
ChatGPT Outage Enterprise Impact: Productivity and Business Continuity
The September outage exposed critical dependencies many organizations developed on ChatGPT for daily operations. Software development teams lost access to code generation and debugging assistance during peak productivity hours. Content creators faced deadline pressures without their primary writing assistance tool. Customer service departments relying on ChatGPT for response drafting experienced immediate efficiency drops.
Financial markets showed no direct impact from the outage, but productivity software companies like Microsoft and Google saw brief trading volume increases as investors speculated about competitive advantages during OpenAI service disruptions. The incident reinforced how AI services have become integral business infrastructure rather than optional productivity enhancements.
Enterprise SLA requirements typically demand 99.9% uptime, translating to maximum 8.77 hours of downtime per year. ChatGPT’s 2025 outage pattern already exceeded these thresholds by mid-year, forcing corporate IT departments to reassess single-vendor AI strategies. Risk management frameworks began incorporating AI service continuity as a critical business function.
Immediate Response Strategies During ChatGPT Outages
When ChatGPT experiences outages, immediate response protocols help minimize productivity impact. First, verify the outage scope by checking OpenAI’s status page monitoring tools and third-party services like DownDetector for real-time user reports. Distinguishing between local connectivity issues and global outages determines appropriate response strategies.
API users should implement automated failover detection through health check endpoints. Testing alternative API keys or switching to different model endpoints can isolate the problem to specific services versus complete platform failure. For comprehensive error handling, refer to our ChatGPT API error codes guide. Enterprise teams benefit from pre-configured fallback scripts that automatically route requests to backup providers when primary services become unavailable.
During the September 3 outage, users who maintained active sessions in mobile applications experienced better service continuity than web interface users. This suggests keeping multiple access methods available as a short-term workaround strategy. Browser refresh cycles and app restarts often restored functionality during partial recovery phases.
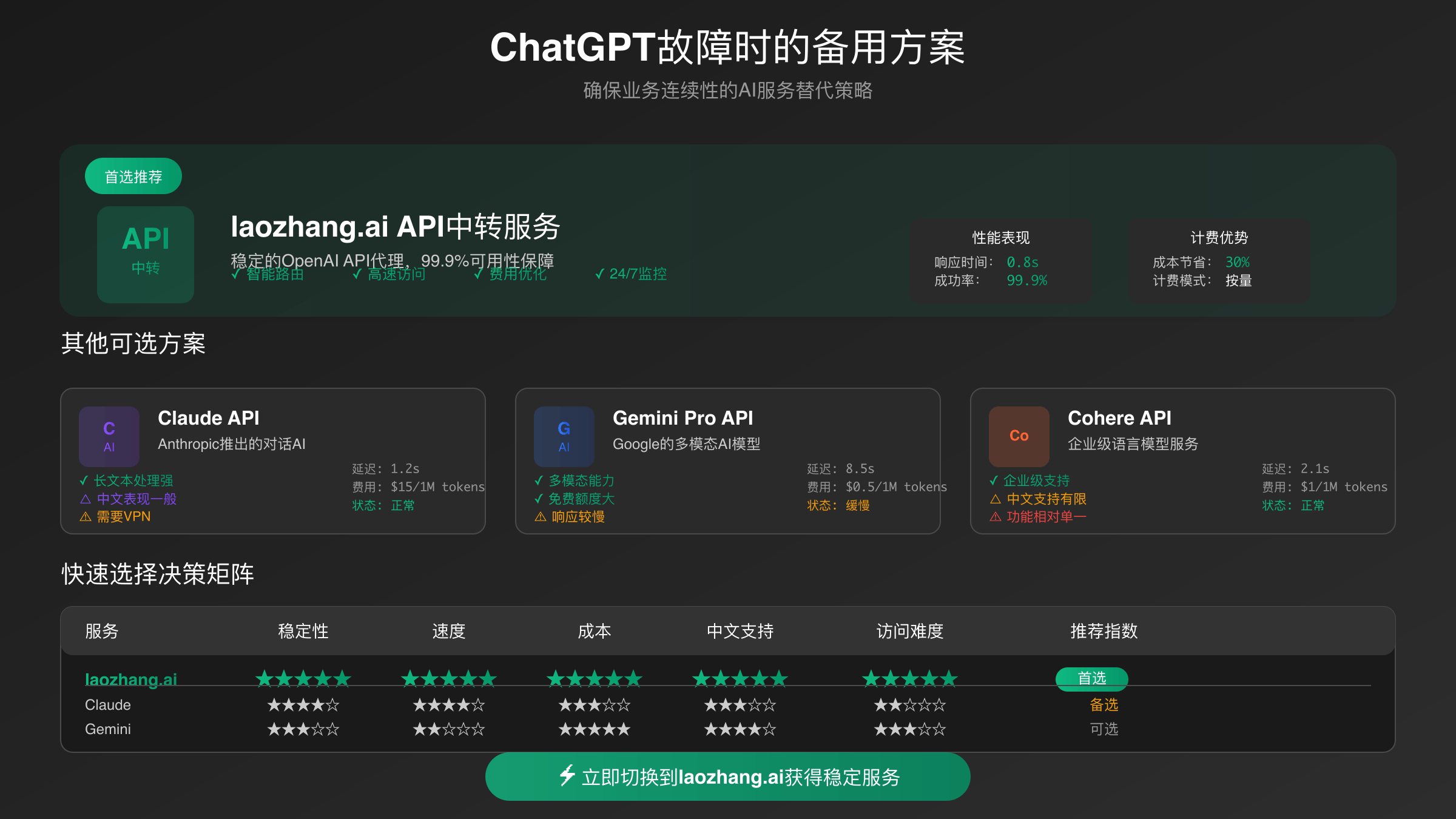
ChatGPT Down Alternative Services: Building Redundant Systems
Enterprise resilience requires maintaining relationships with multiple AI service providers to prevent single points of failure. Anthropic’s Claude API service offers sophisticated reasoning capabilities with different strengths in analytical tasks and ethical considerations. Google’s Gemini API provides seamless integration with Workspace tools and excels at multimodal processing combining text, images, and documents.
Microsoft Copilot presents compelling advantages for organizations already invested in Office 365 ecosystems, offering integrated AI assistance directly within familiar productivity applications. The service maintains separate infrastructure from OpenAI’s consumer-facing ChatGPT, providing additional isolation from outages affecting the primary platform.
Specialized API services like laozhang.ai deliver enterprise-grade reliability with custom rate limiting solutions and dedicated support channels. These services often maintain relationships with multiple underlying model providers, automatically routing requests to available systems during outages. For development teams requiring consistent API availability, such services provide crucial business continuity capabilities.
ChatGPT Outage API Backup Solutions: Technical Implementation
Implementing robust API backup systems requires careful architecture planning and proactive configuration management. Load balancing between multiple AI service providers should include health monitoring, automatic failover logic, and request routing based on service availability. Modern applications benefit from circuit breaker patterns that detect service degradation and redirect traffic before complete failures occur.
Authentication management across multiple providers requires secure credential storage and rotation policies. Each backup service may implement different authentication methods, rate limiting schemes, and response formats. Standardizing these variations through wrapper APIs or middleware layers simplifies application code while maintaining provider flexibility.
Cost optimization strategies should account for redundancy expenses versus outage impact. Maintaining warm standby relationships with backup providers typically involves minimum monthly commitments or setup fees. Organizations must balance these ongoing costs against potential revenue losses during primary service outages. For budget-conscious developers, consider exploring our OpenAI API purchase guide for cost-effective API access options.
ChatGPT Service Monitoring Systems for Outage Prevention
Proactive monitoring systems detect AI service degradation before complete outages impact business operations. Synthetic transaction testing should include representative prompts that exercise key functionality areas like code generation, content creation, and analytical reasoning. Response time thresholds, error rates, and quality metrics provide early warning indicators of service stress.
Alert escalation procedures should distinguish between minor performance degradation and critical service failures. Automated notifications through Slack, email, or SMS ensure relevant teams receive timely outage information. Integration with incident management platforms like PagerDuty or Opsgenie provides structured response workflows during AI service disruptions.
Historical performance data enables pattern recognition and capacity planning. Tracking outage frequency, duration, and root causes helps organizations make informed decisions about service provider relationships and backup investment levels. This data becomes crucial for vendor negotiations and service level agreement discussions.
Preventing ChatGPT Outage Issues: Long-term Reliability Strategies
Building sustainable AI infrastructure requires moving beyond reactive outage response toward proactive resilience planning. Multi-cloud strategies distribute risk across different providers and geographic regions, reducing impact from regional failures or provider-specific issues. Organizations should evaluate AI services as critical infrastructure requiring the same redundancy planning as databases, authentication systems, and network services.
Vendor relationship management becomes increasingly important as AI services mature. Maintaining executive-level relationships with multiple providers ensures priority support during crisis situations and early access to new reliability features. Service level agreements should include specific outage remediation, communication protocols, and financial penalties for extended downtime.
Internal capability development provides ultimate backup through on-premises or hybrid AI deployments. While not matching the scale and sophistication of cloud services, local models can handle basic functionality during external provider outages. This approach requires significant technical investment but offers complete control over service availability.
Cost-Benefit Analysis: Redundancy vs. Risk
Quantifying AI service outage impact helps justify redundancy investments and guide provider selection decisions. Direct costs include lost productivity, missed deadlines, and potential revenue impact from customer-facing AI features. Indirect costs encompass reputation damage, customer satisfaction decline, and competitive disadvantage during extended outages.
Redundancy costs vary significantly based on chosen architecture and provider relationships. Maintaining hot standby services with full feature parity costs more but provides instant failover capabilities. Cold standby approaches reduce ongoing expenses while accepting longer recovery times. Organizations must align redundancy investment with business impact tolerance and recovery time objectives.
Risk assessment should consider outage frequency trends, provider financial stability, and competitive landscape evolution. The 2025 pattern of increased ChatGPT outages suggests reliability challenges may continue as demand scales. Diversifying AI service dependencies reduces exposure to any single provider’s operational challenges.
Future-Proofing AI Infrastructure
The September 2025 ChatGPT outage demonstrates the importance of treating AI services as critical business infrastructure requiring comprehensive backup planning. As organizations increase AI dependency for core business functions, single points of failure become unacceptable risks. Future AI infrastructure must prioritize redundancy, monitoring, and rapid failover capabilities.
Emerging standards for AI service reliability will likely include industry-specific uptime requirements, standardized health monitoring APIs, and improved inter-provider compatibility. Organizations investing in AI infrastructure today should consider these evolving standards when designing backup systems and vendor relationships.
The lesson from 2025’s outage pattern is clear: reliable AI infrastructure requires the same engineering rigor applied to other critical business systems. Proactive planning, redundant providers, and comprehensive monitoring provide the foundation for sustainable AI-dependent operations in an uncertain service landscape.