ChatGPT Plus Usage Limits 2025: Complete Guide to Message Caps and Optimization
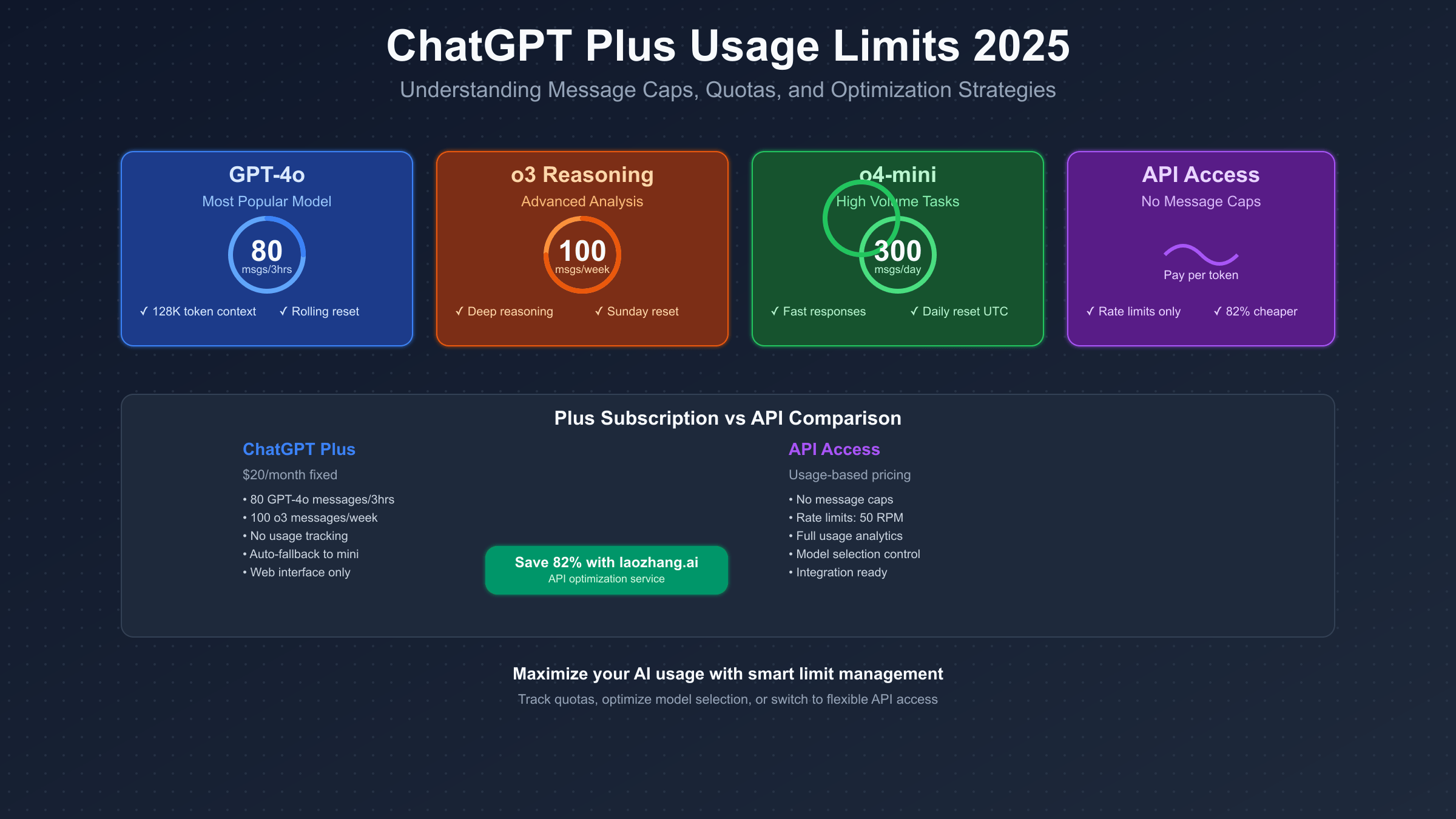
ChatGPT Plus enforces usage limits of 80 messages per 3 hours for GPT-4o, 100 weekly messages for o3, and 300 daily messages for o4-mini. These rolling quotas reset continuously, not at fixed times, making quota management crucial for consistent access.
What Are ChatGPT Plus Usage Limits in 2025?
ChatGPT Plus usage limits represent OpenAI’s resource allocation system that balances computational costs with user access. As of July 2025, the platform implements a sophisticated quota system across six different models, each with unique capabilities and corresponding message allowances. These limits underwent significant changes in April 2025 when OpenAI doubled the allocations for their most popular models, responding to user demand and infrastructure improvements.
The current quota structure reflects a careful balance between model complexity and availability. GPT-4o, the flagship model, provides 80 messages every 3 hours through a rolling window system. This doubled allocation from the previous 40 messages represents OpenAI’s confidence in their infrastructure scaling. The o3 reasoning model offers 100 messages per week, acknowledging its intensive computational requirements for chain-of-thought processing. Meanwhile, o4-mini delivers 300 messages daily for high-volume, routine tasks.
Understanding these limits requires recognizing the technical constraints behind them. Each model interaction consumes significant GPU resources, with costs varying dramatically based on model architecture. GPT-4o processes require high-end NVIDIA H100 GPUs, while o4-mini runs efficiently on less powerful hardware. This hardware allocation directly influences the quota structure, explaining why unlimited access remains exclusive to the $200/month Pro tier. For a comprehensive breakdown of ChatGPT Plus pricing tiers and their corresponding benefits, understanding these technical constraints becomes crucial.
The quota system also includes several hidden complexities that affect real-world usage. Custom GPTs, plugin interactions, and Advanced Data Analysis all count against your message limits, sometimes consuming multiple messages per interaction. Additionally, the system implements context accumulation penalties where longer conversations exponentially increase token consumption, effectively reducing your available messages as conversations progress.
GPT-4o Usage Limits: 80 Messages Every 3 Hours Explained
GPT-4o’s 80-message limit operates through a sophisticated rolling window mechanism that continuously tracks your usage over the previous 180 minutes. Unlike traditional fixed-window rate limiting that resets at specific times, this system evaluates your message history in real-time, providing a more flexible but complex quota management challenge. Each time you send a message, the system checks how many messages you’ve sent in the last three hours and determines whether you’ve exceeded the threshold.
The rolling window implementation prevents the “thundering herd” problem that would occur if all users’ limits reset simultaneously. Instead of everyone rushing to use their quota at midnight UTC, the system distributes load naturally across time zones and usage patterns. This design choice benefits infrastructure stability but requires users to develop more sophisticated usage strategies. A message sent at 2:00 PM only becomes available again at 5:00 PM, creating a continuous cycle of availability and restriction.
Peak performance characteristics of GPT-4o justify its restricted access. The model processes 128,000 tokens of context, enabling complex multi-turn conversations and document analysis. However, this capability comes at a cost – each GPT-4o query consumes approximately 2.5x the computational resources of standard GPT-4. For a detailed comparison between GPT-4o vs GPT-4 capabilities and performance metrics, the resource requirements become evident. During high-demand periods, OpenAI may temporarily reduce limits further, though they rarely communicate these adjustments transparently.
# Calculate remaining GPT-4o messages in rolling window
from datetime import datetime, timedelta
from collections import deque
class GPT4oLimitTracker:
def __init__(self):
self.messages = deque()
self.limit = 80
self.window = timedelta(hours=3)
def can_send_message(self):
current_time = datetime.now()
cutoff_time = current_time - self.window
# Remove messages outside the 3-hour window
while self.messages and self.messages[0] < cutoff_time:
self.messages.popleft()
return len(self.messages) < self.limit
def send_message(self):
if self.can_send_message():
self.messages.append(datetime.now())
return True, self.limit - len(self.messages)
return False, 0
Common scenarios rapidly drain GPT-4o quota despite the increased 80-message allowance. Code debugging sessions, where each iteration requires model analysis, can consume 20-30 messages within an hour. Academic research involving document analysis might use 40-50 messages for a single paper review. Content creation workflows, particularly those requiring multiple revisions, often hit limits within 90 minutes of intensive work. Understanding these consumption patterns helps users plan their high-priority tasks during periods of maximum quota availability.
Understanding o3 Reasoning Model Weekly Limits
The o3 reasoning model's 100 messages per week represents a fundamentally different approach to quota management compared to other ChatGPT Plus models. This weekly allocation resets every Sunday at 00:00 UTC, providing a predictable but restrictive access pattern for OpenAI's most computationally intensive model. The extended reset period reflects the extraordinary resources required for o3's chain-of-thought reasoning, where a single query might internally generate dozens of reasoning steps before producing a response.
Behind each o3 interaction lies a complex reasoning process that can consume 10-50x more computational resources than standard models. The model doesn't simply generate responses; it constructs detailed reasoning chains, evaluates multiple solution paths, and performs internal verification steps. This process might involve generating thousands of internal tokens that users never see, explaining why OpenAI limits access so strictly despite user demand for more extensive reasoning capabilities.
Strategic usage of o3 requires careful task selection and timing. The model excels at complex mathematical proofs, multi-step logical reasoning, advanced code architecture decisions, and nuanced ethical considerations. However, using o3 for simple queries wastes precious weekly quota on tasks that GPT-4o or o4-mini could handle adequately. Successful users develop a task classification system, reserving o3 exclusively for problems requiring deep analytical thinking or complex reasoning chains.
The weekly reset creates unique usage patterns among Plus subscribers. Many users exhaust their o3 quota within the first 2-3 days after Sunday's reset, leaving them without access to advanced reasoning for the remainder of the week. This feast-or-famine cycle encourages users to batch complex tasks for early-week execution or consider API alternatives that offer more consistent access to reasoning capabilities. For those ready to explore API options, our comprehensive ChatGPT API guide explains the transition process, including how services like laozhang.ai provide usage-based pricing with significant discounts.
o4-mini Daily Usage Limits and Reset Times
The o4-mini model provides 300 messages per day with a reset at 00:00 UTC, positioning itself as the high-volume workhorse of the ChatGPT Plus ecosystem. This generous daily allowance reflects o4-mini's optimized architecture, which uses quantization techniques and reduced parameter counts to deliver responsive performance on less powerful hardware. Understanding the UTC reset timing becomes crucial for users across different time zones who need to maximize their daily quota utilization.
UTC-based resets create varying user experiences depending on geographic location. Users in California experience resets at 4:00 PM PST (5:00 PM PDT), potentially splitting their workday across two quota periods. European users see resets during early morning hours, providing fresh quota for the business day. Asian users face resets during business hours, requiring careful planning to avoid disruption. This temporal distribution significantly impacts usage strategies and productivity patterns.
o4-mini excels at specific use cases that benefit from its efficiency-focused design. The model handles routine tasks like email drafting, basic code completion, simple translations, and straightforward question-answering with remarkable speed. Its 128,000-token context window matches larger models, enabling substantial document processing despite its "mini" designation. However, users should recognize tasks where o4-mini falls short: complex reasoning, nuanced creative writing, and sophisticated technical analysis often produce subpar results compared to GPT-4o.
Fallback strategies become essential when approaching o4-mini's daily limit. Unlike GPT-4o's rolling window, the fixed daily reset encourages users to front-load important tasks early in their quota period. Some users maintain task queues, prioritizing high-value activities for fresh quota periods while deferring less critical work. Others leverage the unlimited GPT-4o-mini fallback, though this requires accepting significant quality degradation for complex tasks. The key lies in understanding which tasks genuinely require o4-mini's capabilities versus those that can tolerate the fallback model.
How ChatGPT Plus Usage Limits Actually Work
The technical implementation of ChatGPT Plus usage limits involves multiple layers of sophisticated rate limiting algorithms working in concert. At the core, OpenAI employs a distributed rate limiting system that tracks user requests across multiple data centers while maintaining consistency. This system must handle millions of concurrent users while ensuring fair resource allocation and preventing abuse. The implementation combines elements of token bucket algorithms, sliding window counters, and distributed consensus mechanisms, as detailed in OpenAI's official rate limits documentation.
Token consumption patterns reveal hidden complexities in how limits actually deplete. Each message doesn't simply count as one unit against your quota; instead, the system calculates token usage based on input length, output length, and context size. A conversation's first message might consume 500 tokens, but the 20th message in the same conversation could consume 5,000 tokens due to accumulated context. This exponential growth in token consumption effectively reduces your message count as conversations progress, creating a non-linear depletion of quotas.
# Demonstration of token accumulation in conversations
def calculate_conversation_tokens(messages, base_tokens=500):
"""Calculate cumulative token usage in a conversation"""
total_tokens = 0
context_tokens = 0
for i, message in enumerate(messages):
# Each message includes its own tokens plus all previous context
message_tokens = base_tokens
context_tokens += message_tokens
# Context grows with each exchange (user + assistant)
if i > 0:
total_tokens += context_tokens + message_tokens
else:
total_tokens += message_tokens
print(f"Message {i+1}: {context_tokens + message_tokens} tokens")
return total_tokens
# Example: 10-message conversation
messages = range(10)
total = calculate_conversation_tokens(messages)
print(f"\nTotal tokens for conversation: {total}")
print(f"Average tokens per message: {total / 10}")
Hidden multipliers significantly impact perceived usage limits. When using ChatGPT's web browsing capability, each search and page retrieval counts as additional messages against your quota. The DALL-E integration consumes messages for image generation requests. Code interpreter sessions multiply consumption through file operations and execution steps. Advanced Data Analysis can consume 3-5 messages for complex data processing tasks. These hidden costs mean that 80 GPT-4o messages might translate to only 20-30 actual user interactions when using advanced features.
The system also implements various safeguards and quality-of-service mechanisms that affect limit behavior. During high-load periods, OpenAI may implement "soft throttling" where response times increase before hard limits engage. The platform maintains separate quotas for different feature sets, meaning you might exhaust GPT-4o chat limits while retaining access to GPT-4o through Custom GPTs. Understanding these nuances helps explain why users sometimes experience inconsistent limit behavior across different ChatGPT interfaces and features.
Track Your ChatGPT Plus Usage Limits Like a Pro
Professional usage tracking for ChatGPT Plus requires implementing systematic monitoring since OpenAI provides no native quota visibility. Users must develop their own tracking methodologies to avoid unexpected limit encounters during critical work. The absence of an official API or dashboard for quota monitoring represents a significant usability gap that power users must bridge through custom solutions. This limitation drives many professionals to create elaborate tracking systems or consider API alternatives with transparent usage metrics.
Manual tracking methods range from simple spreadsheets to sophisticated browser extensions. The most basic approach involves maintaining a timestamp log of each interaction, calculating rolling windows for GPT-4o, and daily counts for other models. However, manual tracking becomes tedious and error-prone during intensive usage sessions. More advanced users employ browser bookmarklets that inject tracking interfaces directly into the ChatGPT interface, automatically logging interactions and calculating remaining quotas.
![]()
Building an automated usage dashboard provides the most reliable tracking solution. By intercepting browser network requests or using browser automation tools, you can create real-time usage monitors that display remaining quotas, predict limit encounters, and suggest optimal model switching strategies. These dashboards can integrate with productivity tools, sending alerts when quotas approach depletion or when optimal usage windows arrive based on your historical patterns.
// Browser console script for basic usage tracking
class ChatGPTUsageTracker {
constructor() {
this.usage = JSON.parse(localStorage.getItem('chatgpt_usage') || '{}');
this.initializeTracking();
}
initializeTracking() {
// Hook into ChatGPT's message sending
const originalFetch = window.fetch;
window.fetch = async (...args) => {
const response = await originalFetch(...args);
if (args[0].includes('/conversation')) {
this.trackUsage();
}
return response;
};
}
trackUsage() {
const now = new Date();
const model = this.detectCurrentModel();
if (!this.usage[model]) {
this.usage[model] = [];
}
this.usage[model].push(now.toISOString());
this.cleanOldEntries();
localStorage.setItem('chatgpt_usage', JSON.stringify(this.usage));
this.displayRemaining();
}
detectCurrentModel() {
// Detect from UI elements or default to gpt-4o
return document.querySelector('.model-selector')?.textContent || 'gpt-4o';
}
calculateRemaining(model) {
const limits = {
'gpt-4o': { count: 80, window: 3 * 60 * 60 * 1000 },
'o4-mini': { count: 300, window: 24 * 60 * 60 * 1000 }
};
const limit = limits[model];
if (!limit) return null;
const cutoff = new Date() - limit.window;
const recentUsage = this.usage[model]?.filter(timestamp =>
new Date(timestamp) > cutoff
).length || 0;
return limit.count - recentUsage;
}
displayRemaining() {
console.log('=== ChatGPT Plus Usage ===');
Object.keys(this.usage).forEach(model => {
const remaining = this.calculateRemaining(model);
if (remaining !== null) {
console.log(`${model}: ${remaining} messages remaining`);
}
});
}
}
// Initialize tracker
const tracker = new ChatGPTUsageTracker();
Predictive usage calculations enhance tracking beyond simple counting. By analyzing your historical usage patterns, you can predict when you'll hit limits and proactively adjust behavior. Machine learning models can identify your peak usage hours, typical conversation lengths, and feature utilization patterns. This predictive capability enables preemptive model switching, conversation splitting, and workload distribution strategies that maximize productivity within quota constraints.
ChatGPT Plus Usage Limits vs API Rate Limits
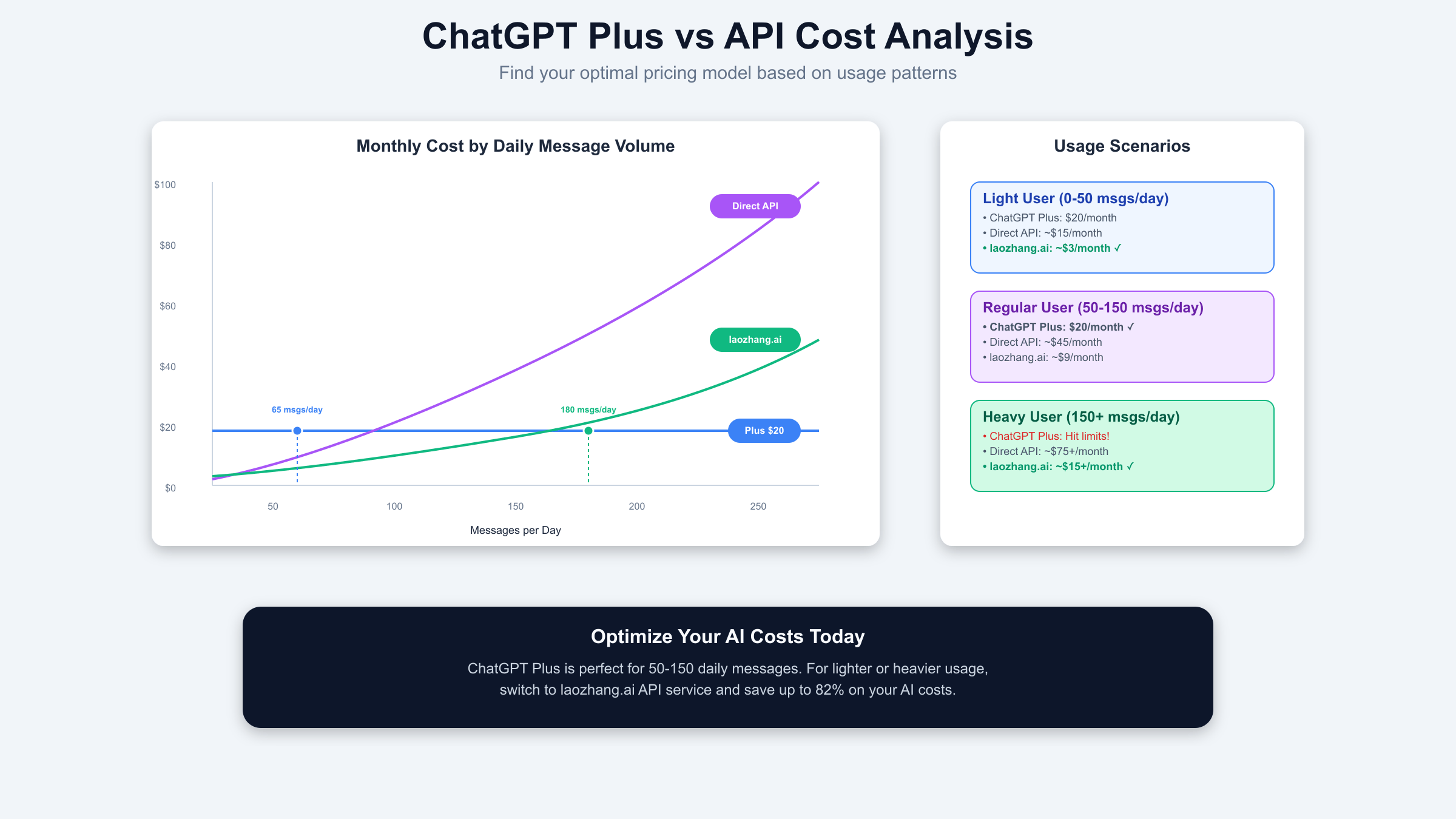
The fundamental difference between ChatGPT Plus usage limits and API rate limits lies in their billing and restriction models. ChatGPT Plus operates on a fixed $20 monthly subscription with hard message caps, while API access uses pay-per-token pricing with rate limits measured in requests per minute (RPM) and tokens per minute (TPM). This structural difference creates distinct use cases and cost-effectiveness profiles that vary dramatically based on usage patterns.
API rate limits provide more flexibility but require careful cost management. Standard tier-2 API access allows 25 requests per minute for o3 models and 60,000 tokens per minute for GPT-4o. These limits increase with usage tier progression, eventually reaching 50 RPM and 150,000 TPM at higher tiers. Unlike Plus message caps that completely block access when exceeded, API rate limits simply throttle request speed, allowing continuous operation at reduced throughput. This distinction proves crucial for production applications requiring consistent availability. For a comprehensive understanding of how different models perform under these constraints, see our detailed OpenAI models comparison.
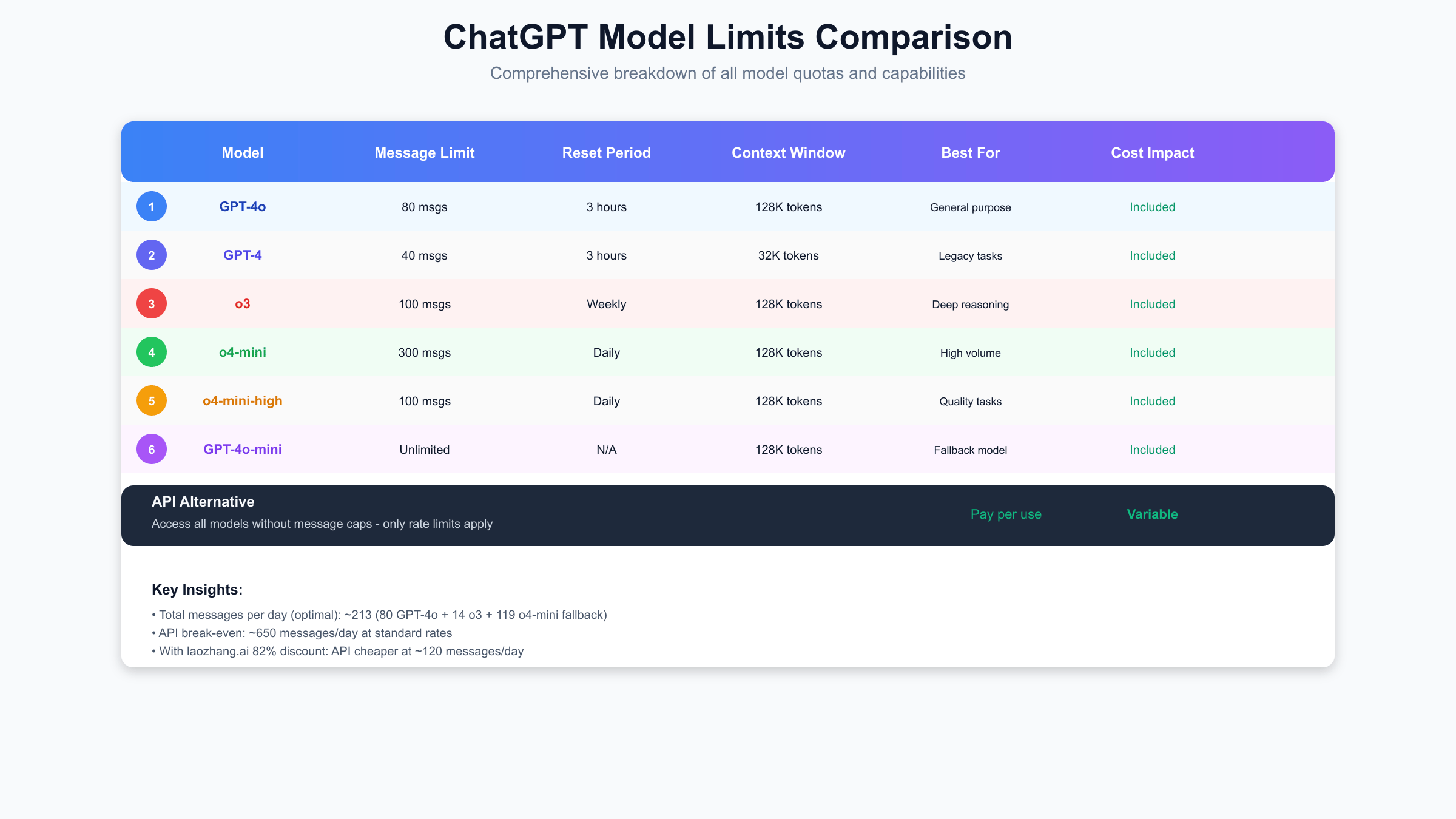
Cost analysis reveals surprising breakpoints between Plus and API pricing. For light users sending fewer than 65 messages daily, API access through services like laozhang.ai (offering 82% discount from standard pricing) costs approximately $3-5 monthly compared to Plus's fixed $20. Medium users (65-180 daily messages) find Plus cost-effective, saving $10-25 monthly versus API costs. Heavy users exceeding 180 daily messages face a dilemma: Plus limits become restrictive, but API costs can exceed $50 monthly even with discounted pricing. Understanding these breakpoints is crucial for AI cost optimization strategies that maximize value while maintaining necessary capabilities.
# Cost comparison calculator for Plus vs API
def calculate_optimal_service(daily_messages, avg_tokens_per_message=1000):
"""Determine most cost-effective option based on usage"""
# Pricing constants (July 2025)
PLUS_MONTHLY = 20
API_PRICE_PER_1K = 0.01 # GPT-4o standard
LAOZHANG_DISCOUNT = 0.82
# Calculate monthly API cost
monthly_tokens = daily_messages * avg_tokens_per_message * 30
api_cost_standard = (monthly_tokens / 1000) * API_PRICE_PER_1K
api_cost_laozhang = api_cost_standard * (1 - LAOZHANG_DISCOUNT)
# Plus limitations check
plus_daily_capacity = 213 # Optimal mix of all models
plus_sufficient = daily_messages <= plus_daily_capacity
analysis = {
'daily_messages': daily_messages,
'plus_cost': PLUS_MONTHLY,
'api_standard_cost': round(api_cost_standard, 2),
'api_laozhang_cost': round(api_cost_laozhang, 2),
'plus_sufficient': plus_sufficient,
'recommendation': ''
}
if daily_messages < 65:
analysis['recommendation'] = f'Use laozhang.ai API (save ${PLUS_MONTHLY - api_cost_laozhang:.2f}/month)'
elif daily_messages <= plus_daily_capacity:
analysis['recommendation'] = f'Use ChatGPT Plus (save ${api_cost_laozhang - PLUS_MONTHLY:.2f}/month)'
else:
analysis['recommendation'] = f'Must use API - Plus limits insufficient. Consider laozhang.ai for 82% savings'
return analysis
# Example calculations
for messages in [30, 100, 200, 500]:
result = calculate_optimal_service(messages)
print(f"\n{messages} messages/day: {result['recommendation']}")
print(f" Plus: ${result['plus_cost']}, API: ${result['api_laozhang_cost']}")
The laozhang.ai API service emerges as a compelling alternative for users seeking flexibility without standard API pricing burdens. By offering an 82% discount from OpenAI's standard rates, it creates new breakpoints where API access becomes economically viable. Users frustrated by Plus limits can access the same models through laozhang.ai's infrastructure, paying only for actual usage while avoiding the psychological burden of watching message counts. The service particularly benefits international users who face payment difficulties with OpenAI's limited payment options.
Optimize Your ChatGPT Plus Usage Limits Strategy
Optimization strategies for ChatGPT Plus usage limits require systematic approaches that balance model capabilities with quota constraints. The key lies in developing a model selection algorithm that automatically routes queries to the most appropriate model based on task complexity, remaining quota, and time until reset. This algorithmic approach prevents wasteful usage of premium models on simple tasks while ensuring complex queries receive adequate computational resources.
Time-based usage distribution leverages the different reset schedules across models to maintain consistent access throughout your workday. By understanding that GPT-4o uses rolling 3-hour windows, o3 resets weekly, and o4-mini resets daily at UTC midnight, you can create usage patterns that ensure critical capabilities remain available when needed. Morning routines might prioritize o4-mini for initial research, midday sessions utilize GPT-4o for complex analysis, while evening work reserves o3 for weekly strategic planning tasks.
Context management techniques dramatically extend effective message limits by controlling token consumption. Rather than maintaining lengthy conversations that exponentially increase token usage, implement a conversation splitting strategy. When context exceeds 8,000 tokens, start fresh conversations with summarized context, reducing per-message token consumption by 60-80%. This approach effectively multiplies your available messages while maintaining conversation continuity through careful context preservation.
# Intelligent model selection algorithm
class OptimalModelSelector:
def __init__(self):
self.quotas = {
'gpt-4o': {'remaining': 80, 'reset_hours': 3},
'o3': {'remaining': 100, 'reset_days': 7},
'o4-mini': {'remaining': 300, 'reset_hours': 24}
}
def select_model(self, task_complexity, urgency='normal'):
"""
Select optimal model based on task complexity (1-10) and urgency
Returns: (model_name, confidence_score)
"""
# Task complexity thresholds
if task_complexity <= 3:
# Simple tasks always use o4-mini if available
if self.quotas['o4-mini']['remaining'] > 10:
return 'o4-mini', 0.95
else:
return 'gpt-4o-mini', 0.90 # Fallback
elif task_complexity <= 6:
# Medium tasks prefer GPT-4o but can use o4-mini
if urgency == 'high' and self.quotas['gpt-4o']['remaining'] > 5:
return 'gpt-4o', 0.90
elif self.quotas['o4-mini']['remaining'] > 50:
return 'o4-mini', 0.75
elif self.quotas['gpt-4o']['remaining'] > 20:
return 'gpt-4o', 0.85
else:
return 'gpt-4o-mini', 0.60
else:
# Complex tasks require o3 or GPT-4o
if task_complexity >= 9 and self.quotas['o3']['remaining'] > 5:
return 'o3', 0.95
elif self.quotas['gpt-4o']['remaining'] > 10:
return 'gpt-4o', 0.80
elif self.quotas['o3']['remaining'] > 0:
return 'o3', 0.90
else:
# Consider API fallback for critical tasks
return 'api-recommended', 0.70
def update_quota(self, model, used=1):
"""Update remaining quota after usage"""
if model in self.quotas:
self.quotas[model]['remaining'] -= used
# Usage example
selector = OptimalModelSelector()
tasks = [
("Draft email", 2, "normal"),
("Debug complex algorithm", 8, "high"),
("Analyze legal document", 7, "normal"),
("Answer simple question", 1, "normal"),
("Design system architecture", 9, "high")
]
for task, complexity, urgency in tasks:
model, confidence = selector.select_model(complexity, urgency)
print(f"{task}: Use {model} (confidence: {confidence})")
selector.update_quota(model)
Automation scripts transform manual optimization into systematic efficiency. By implementing browser automation or ChatGPT API wrappers, users can create intelligent routing systems that automatically select models, manage context, and track usage without manual intervention. These scripts can integrate with productivity tools like Notion or Obsidian, creating seamless workflows that respect quota limits while maximizing output quality. The investment in automation setup pays dividends through sustained productivity and reduced cognitive overhead.
Common ChatGPT Plus Usage Limit Problems and Solutions
The dreaded "You've reached your usage cap" message appears at the worst possible moments, often during critical work sessions. This error occurs when you exceed model-specific quotas, but the generic message provides no indication of which limit triggered the block or when access will resume. Users frequently encounter this limitation mid-conversation, losing context and momentum. The solution requires understanding the specific model that hit its limit and either waiting for the reset window or switching to an available alternative model.
Unexpected quota consumption plagues users who don't understand hidden multipliers in the ChatGPT ecosystem. A single message requesting web browsing might consume 3-5 messages from your quota as the system performs searches and retrieves pages. Code interpreter sessions multiply consumption through execution steps and error corrections. Advanced Data Analysis compounds this effect by combining code execution with data processing. Solutions include disabling unnecessary features, using dedicated tools for web searches, and reserving ChatGPT for core AI interactions rather than auxiliary functions.
Model downgrade issues create quality inconsistencies that frustrate professional users. When GPT-4o limits exhaust, ChatGPT silently falls back to GPT-4o-mini without notification. This automatic downgrade can derail complex analytical tasks, produce inferior code suggestions, or fail at nuanced creative work. Users discover the downgrade only when output quality noticeably degrades. Preventing this requires proactive quota monitoring and manual model selection to ensure critical tasks receive appropriate computational resources.
Multi-account considerations tempt users seeking to circumvent limits, but this approach carries significant risks. OpenAI's terms of service explicitly prohibit creating multiple accounts to bypass usage restrictions. Detection mechanisms identify patterns like shared payment methods, IP addresses, and usage behaviors. Violations can result in account suspension or permanent bans, losing access to all ChatGPT services. Instead of risking account termination, users should explore legitimate alternatives like Team subscriptions for shared quotas or transitioning to API access through authorized providers like laozhang.ai that offer transparent, scalable usage models.
Future of ChatGPT Plus Usage Limits
The trajectory of ChatGPT Plus usage limits through 2025-2026 will likely reflect competitive pressures and infrastructure improvements. Anthropic's Claude Pro offers 5x more usage than ChatGPT Plus for similar pricing, while Google's Gemini Advanced provides generous quotas with multimodal capabilities. This competitive landscape pressures OpenAI to either increase Plus quotas or introduce tiered subscription models that better serve diverse user needs. Market analysis suggests OpenAI may announce significant quota increases by Q4 2025 to maintain competitive positioning.
Infrastructure improvements, particularly the deployment of next-generation AI accelerators and optimized model architectures, will enable more generous quotas without proportional cost increases. OpenAI's reported investments in custom silicon and advanced model compression techniques could reduce per-query computational costs by 50-70% by mid-2026. These efficiency gains would naturally translate to expanded user quotas or new pricing tiers that better align costs with usage patterns.
Tiered subscription possibilities represent the most likely evolution of ChatGPT Plus. Rather than maintaining a single $20 tier with uniform limits, OpenAI may introduce bronze ($20), silver ($50), and gold ($100) tiers with proportionally increased quotas. This structure would retain accessible entry-level pricing while capturing additional revenue from power users currently forced to use expensive API access. Such tiering would compete directly with Anthropic's Pro model while providing clearer upgrade paths for users outgrowing basic Plus limits. Early indicators suggest announcement of new tiers could come as soon as Q3 2025, fundamentally reshaping how users interact with AI assistants.